system architecture
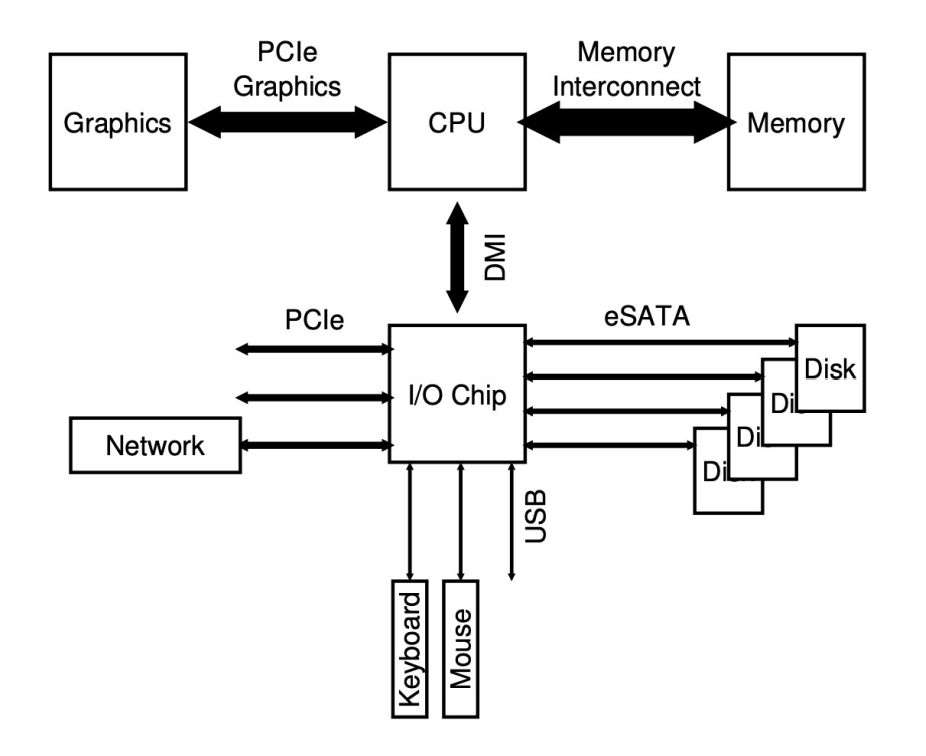
Bus
: data path
▶1. Memory bus
: CPU ↔ memory
▶2. I/O bus
: CPU ↔ I/O devices
- USB(Universal Serial Bus): univsersal
- SCSI, SATA: hard disk만을 위한 bus.
- PCIe: 요즘에 device들은 SCSI, SATA 대신 이걸 많이 사용
canonical device
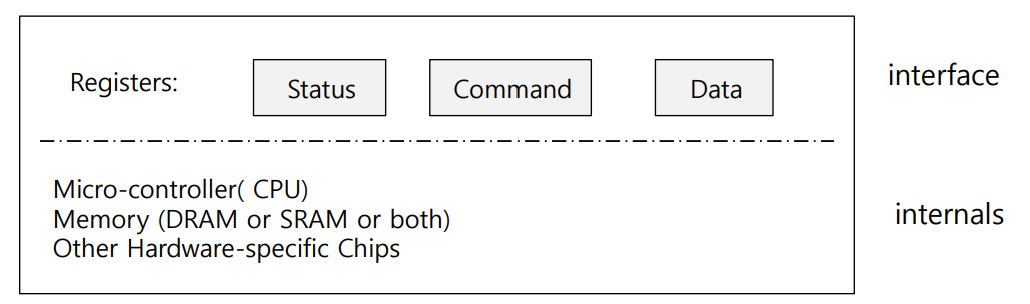
▶interface
OS는 세 register를 read/write함으로써 device의 작동을 컨트롤함. 여기 구조는 device끼리 거의 비슷함
- status register: device의 현재 상태
- command register: device가 특정 task를 수행하도록 함
- data register: 이를 통해 device와 data를 주고받음
▶internals
device의 기능에 따라 달라짐
OS & device의 interaction
process가 I/O를 사용하려 할 때, OS가 구현하는 방식
▶polling
: OS는 device가 준비될 때까지 device의 status register를 반복해서 read하며 device를 기다린다.
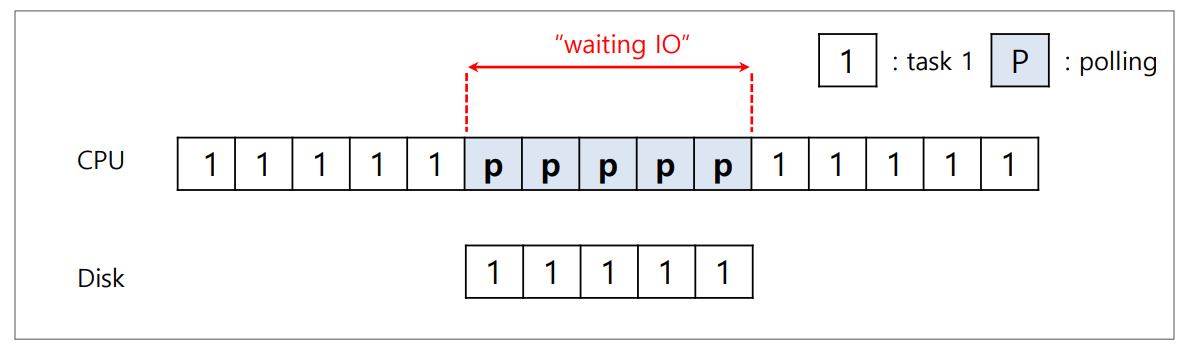
- device를 기다리는 데에 CPU time이 낭비된다.
- device의 수행이 얼마 안 걸리면 -> polling이 낫다.
: device의 수행이 매우 빠른 경우, 이때마다 interrupt가 일어나면 context switch는 아주 expensive하므로 시스템을 매우 느리게 하기 때문이다.
▶interrupts
: I/O를 요청한 프로세스를 sleep시키고 다른 프로세스로 context switch하여 CPU는 다른 task를 하고 있는다. device가 끝나면 interrupt로써 그 프로세스를 깨운다.
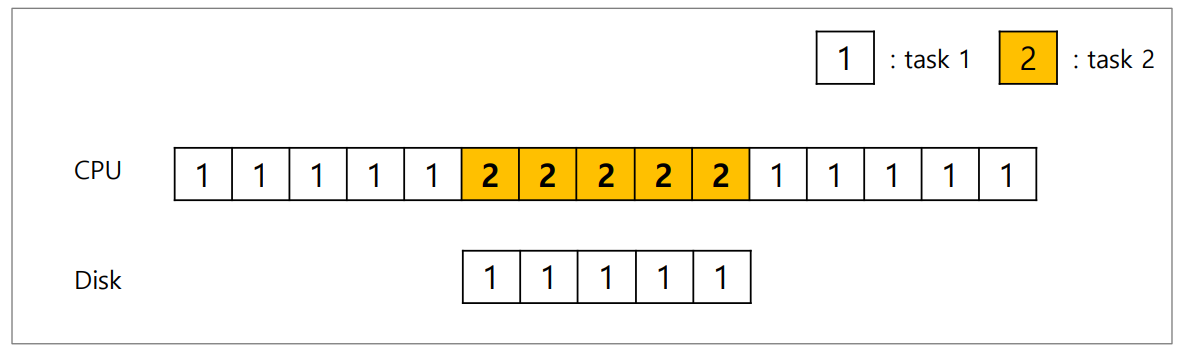
- CPU와 disk가 적절히 utilize된다.
- device의 수행이 오래걸리면 -> interrupts가 낫다.
DMA(Direct Memory Access): HW support
CPU는 memory에 있는 큰 크기의 데이터를 device로 copy할 때 over-burden되어 시간을 많이 소모한다.
아래는 CPU가 copy를 수행하고, I/O request가 발생해 context switch가 일어나며 device가 일을 하고, 다시 원래의 프로세스가 wake up되는 과정이다.
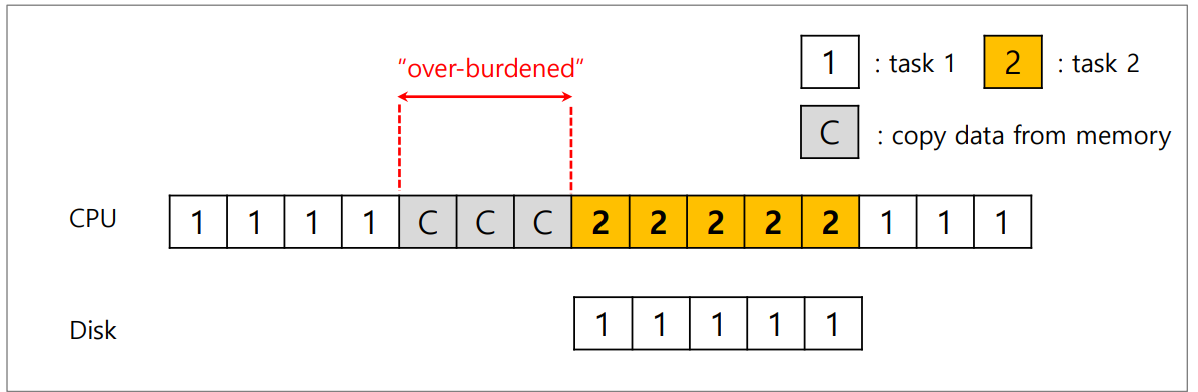
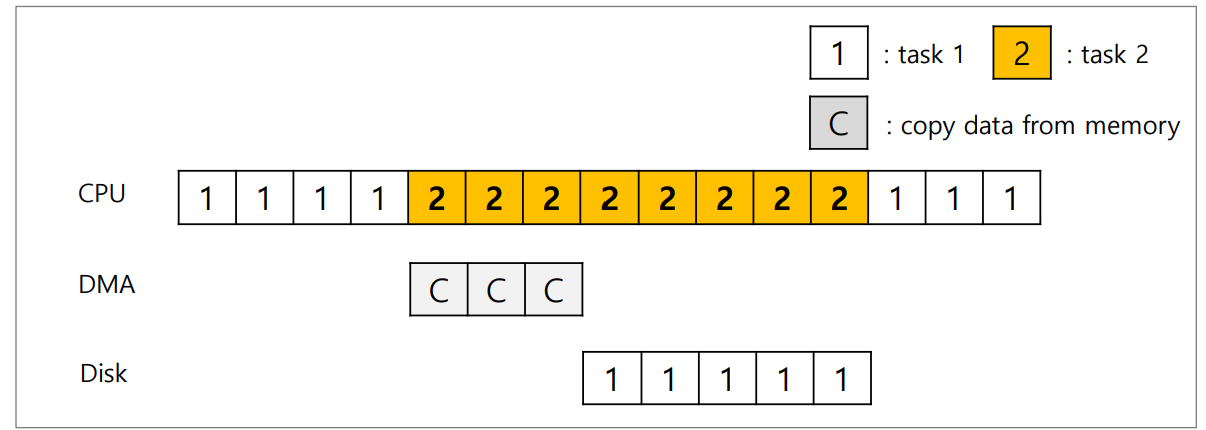
위 문제의 해결을 위한 HW의 support로서 DMA가 있다.
이는 단지 copy 작업을 CPU 대신에 헤주는 것이며, 그동안 CPU는 다른 task를 할 수 있다.
DMA는 copy를 완수하고 interrupt를 일으키며, device는 I/O operation을 수행한다.
OS와 device의 interaction 방식
▶I/O instructions
: OS가 in, out 등의 instruction을 통해 device register와 데이터를 주고받음
▶memory-mapped I/O
: memory에 access하듯이 device에 똑같이 access할 수 있다.
: device register들이 physical address space의 일부를 차지하여,
OS는 memory access를 위한 instruction을 사용해 I/O에도 똑같이 access(: device에 write, device로부터 read)할 수 있다.
abstraction: OS가 다양한 device와 interact할 수 있게 함

- device driver: device와의 interaction이 encapsulate된 OS의 일부분.
- device를 쓰고 싶어하는 appliation은 단지 file system만 보면 됨
'컴퓨터과학 > 컴퓨터구조와 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [File System] File & Directory, Hard link & Soft Link (0) | 2024.06.05 |
|---|---|
| [Secondary Storage] HDD(Hard Disk Drives), RAID(Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| [Memory management] Swapping (0) | 2024.05.23 |
| [Memory management] Paging (0) | 2024.05.13 |
| [Memory management] Memory virtualization, Dynamic relocation, Segmentation (0) | 2024.05.01 |