File
: byte의 선형 배열임
- low-level filename: inode number
create와 remove
▶create

- fd: fild descriptor - 정수값임
▶remove

offset
: read/write을 시작할 파일 내 위치
▶offset에 영향을 주는 함수
- read()
- write()
- lseek(): read/write offset을 재설정
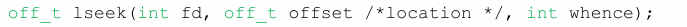
▶traces example

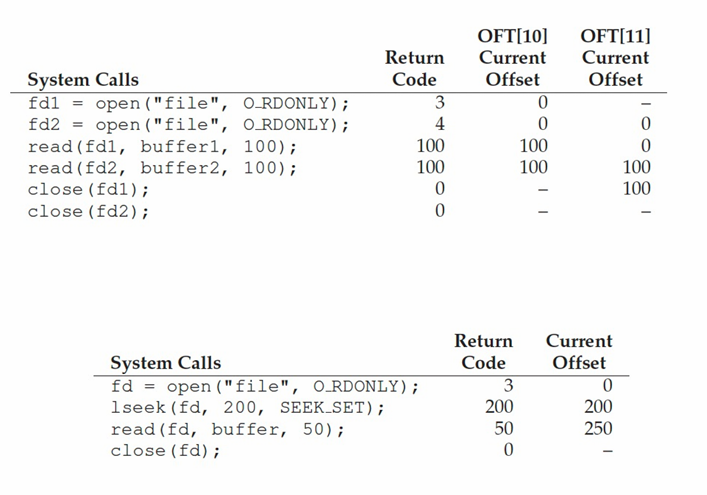
write()와 fsync()
▶write()
: 데이터를 우선 메모리 버퍼에 write하고, '나중에' disk로의 업데이트
▶fsync()
: 즉시 disk에 write함

fork()와 dup()
▶fork()
- child process는 parent process의 file descriptor table을 상속받음
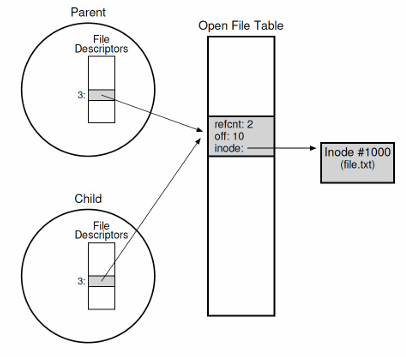
▶dup()
: file descriptor 복제

Directory
: 특별한 구조를 가진 file이라 할 수 있다.
- list of <user-readable filename, low-level filename> pair
directory entry 구조체

make
mkdir()의 결과 빈 directory가 생성되며,
이 안에는 두 entry (자신과 부모)가 있다.

read

Hard link & Soft Link
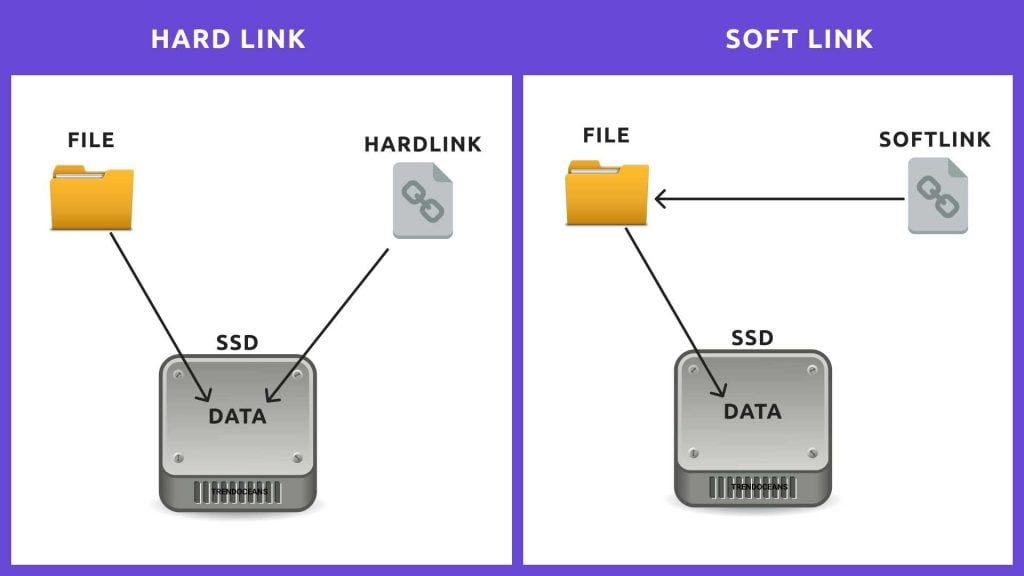
hard link
▶link
기존에 "file"이 있고, 여기에 "file2"라는 hard link를 link하면,
file이 아니라 inode에 link된다. (-> "file1"과 "file2"의 inode값은 같고, name은 다르다.)
- hard link는 file에만 가능하고 directory에는 불가능하다.


▶unlink
: reference count를 감소시킴
fd와 fd2가 동일 inode에 연결되어있는 경우, 이 파일을 삭제하면...
1. 우선 unlink(fd)를 함
i) inode number 내의 reference count(= 2)를 체크
ii) human-readable name과 inode number 간의 link 삭제: fd와 inode 연결 끊김
iii) reference count 1 감소 -> 이때는 아직 file 자체는 남아있음
2. 이제 unlink(fd2)를 함
i) reference count = 1
ii) fd2와 inode 연결 끊김
iii) reference count = 0으로 감소 -> file은 disk에서 물리적으로 삭제됨: inode와 block들을 free

soft link (= symbolic link)
- soft link는 별도의 file type이다.
▶link
기존에 "file"이 있고, 여기에 "file2"라는 soft link를 link하면,
inode가 아니라 file에 link된다.
- soft link는 file과 directory 모두에 가능하다.



'컴퓨터과학 > 컴퓨터구조와 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [File System] FFS(Fast File System) (0) | 2024.06.13 |
|---|---|
| [File System] VSFS(very simple file system) (0) | 2024.06.05 |
| [Secondary Storage] HDD(Hard Disk Drives), RAID(Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| [I/O Devices] I/O Bus, Canonical device, Polling & Interrupt, DMA, MMIO (1) | 2024.06.04 |
| [Memory management] Swapping (0) | 2024.05.23 |